The growth of research with active pupilometry
In recent decades, pupillometry has been useful for healthcare professionals.
Initially, the method was limited to the use of a flashlight aimed at the pupil to assess the impairment of
consciousness.
Advances in technology and the development of devices capable of accurately measuring pupil diameter have
allowed more sophisticated and accurate assessments.
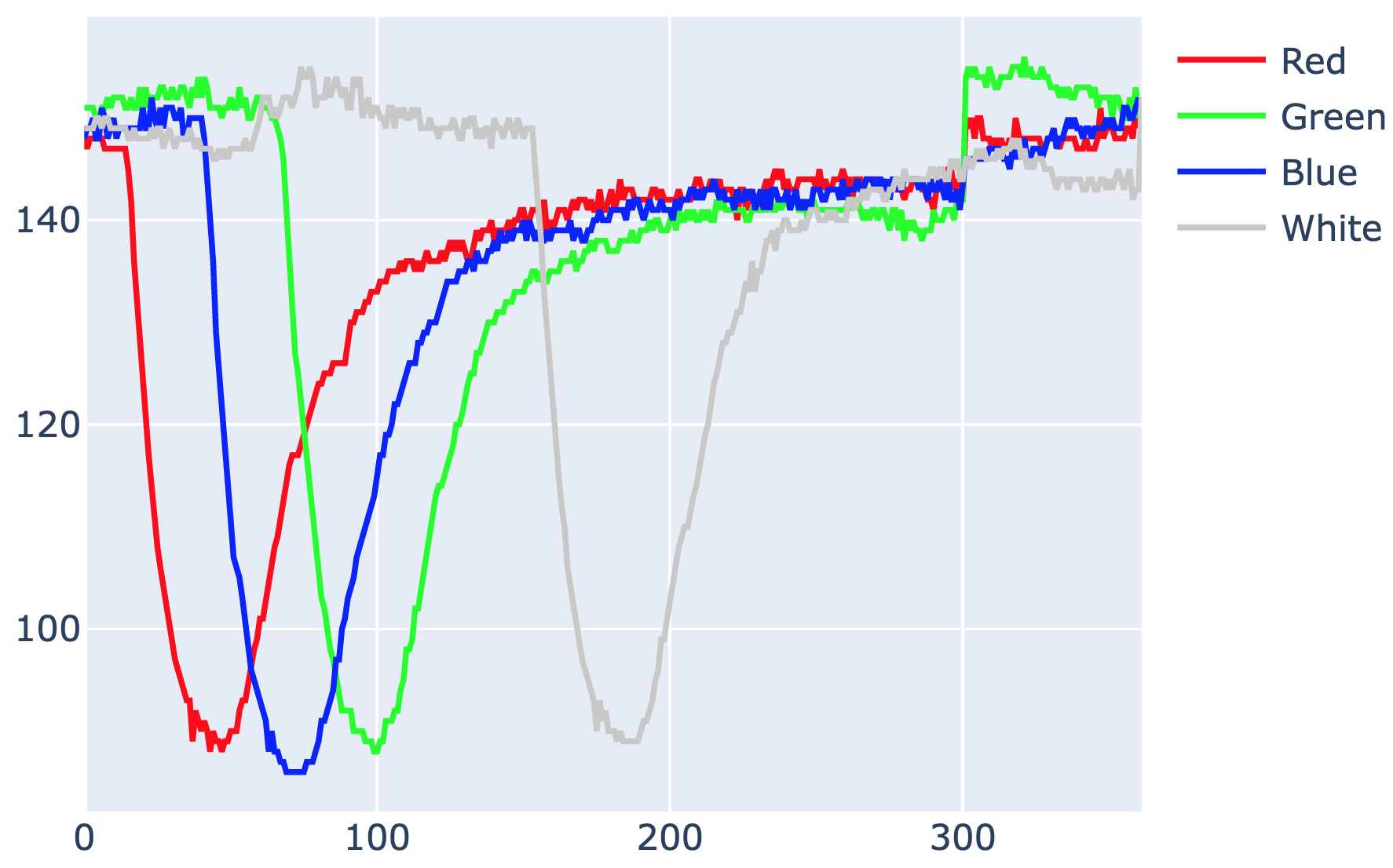
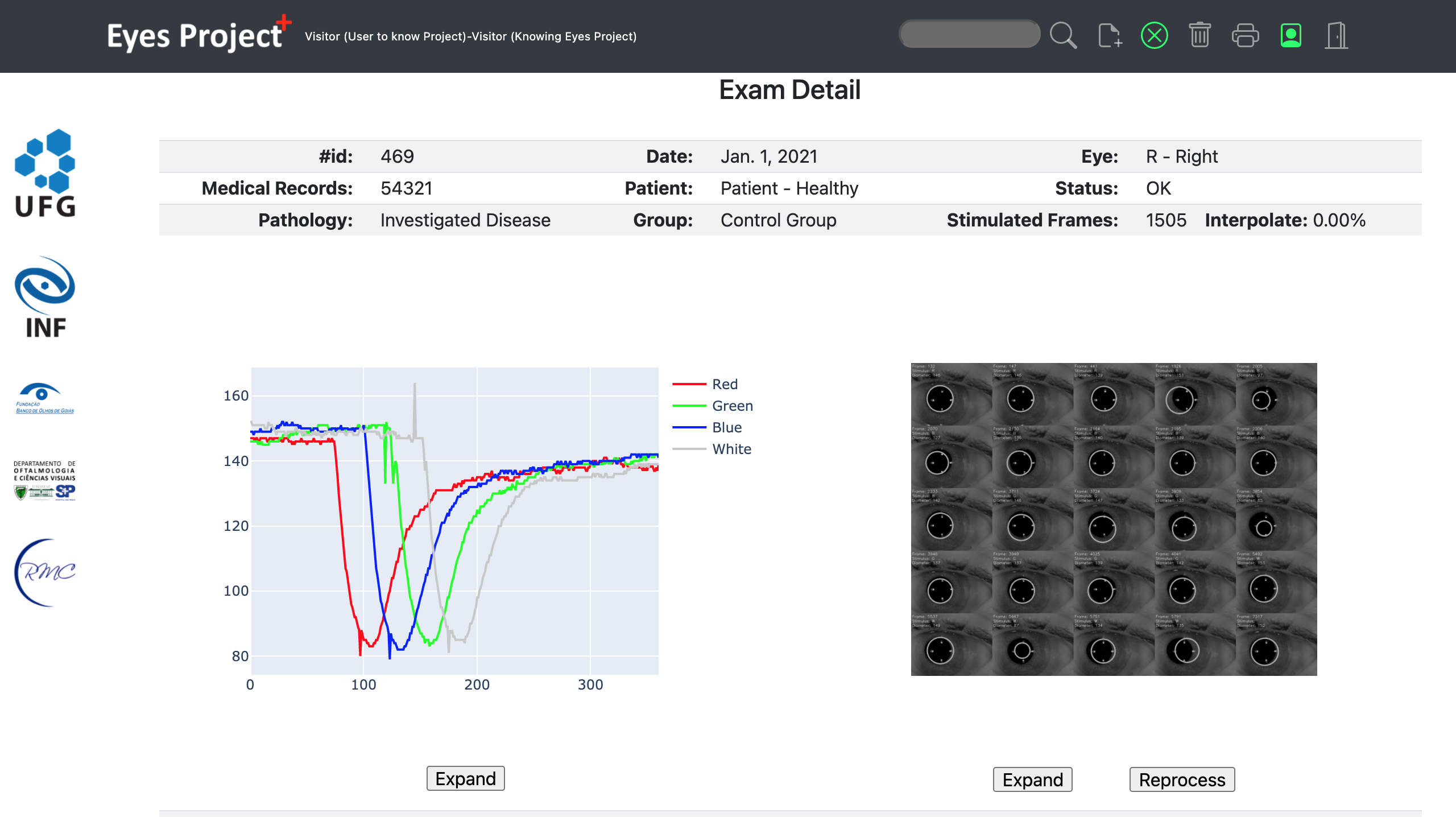
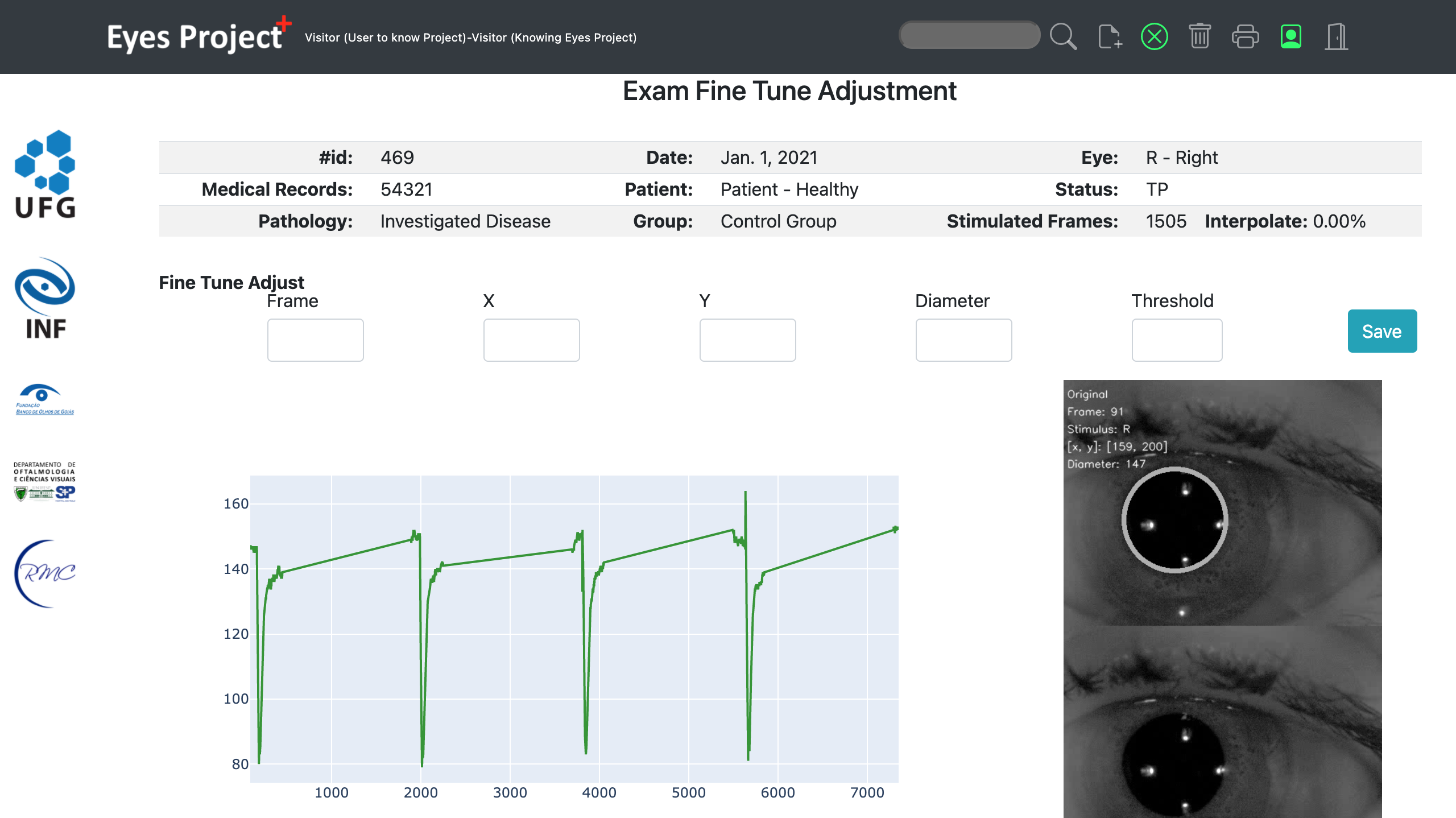
Currently, studies show that pupillary reaction to light can help specialists make different types of
diagnoses.
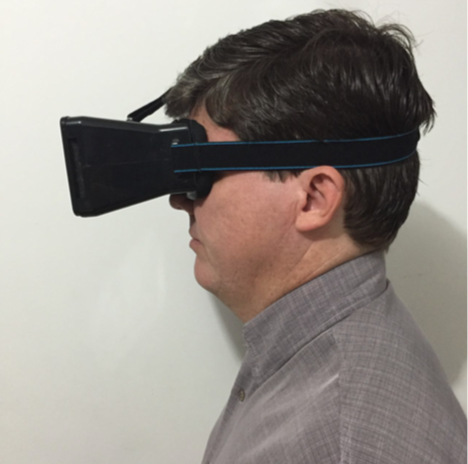
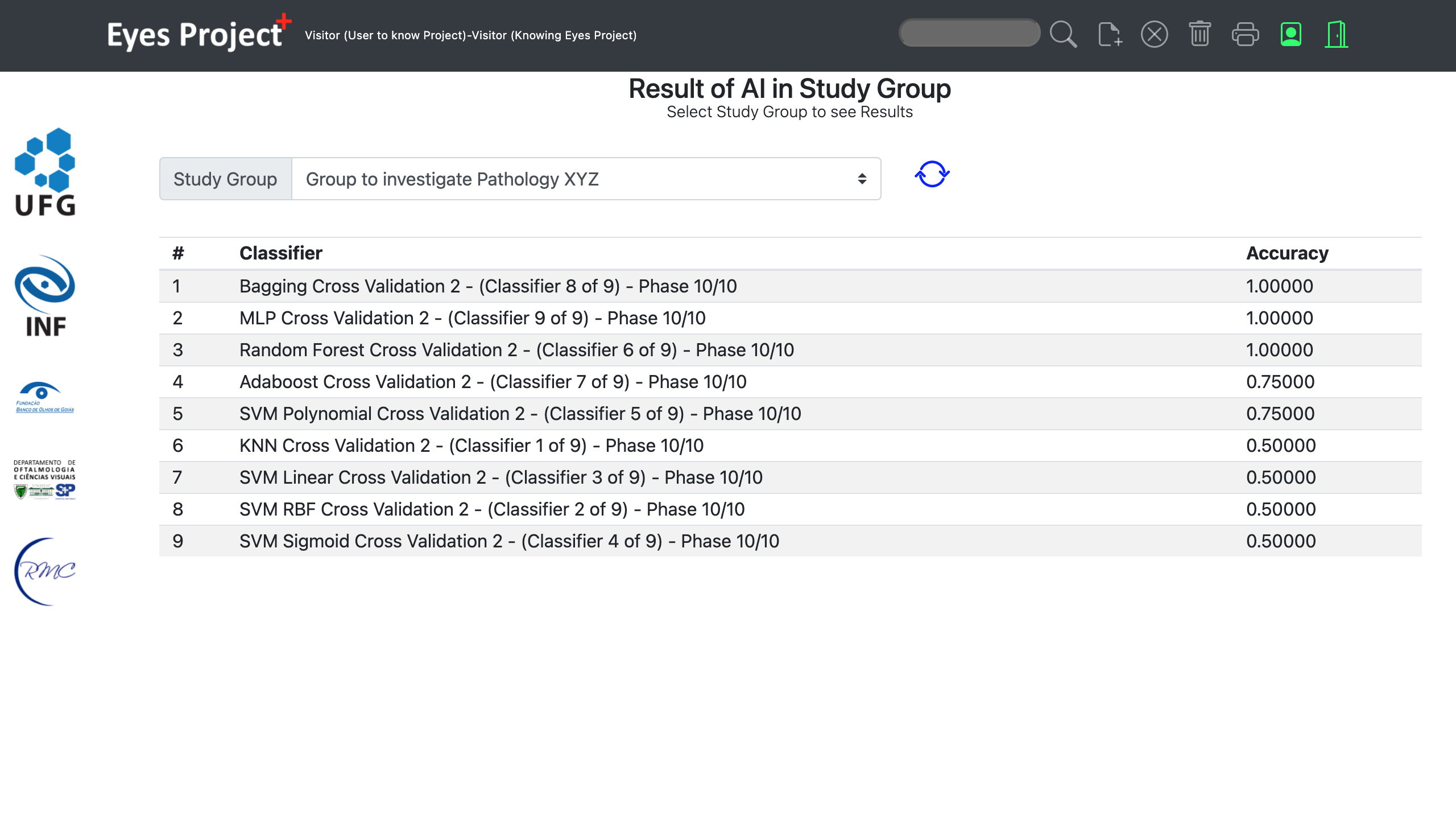
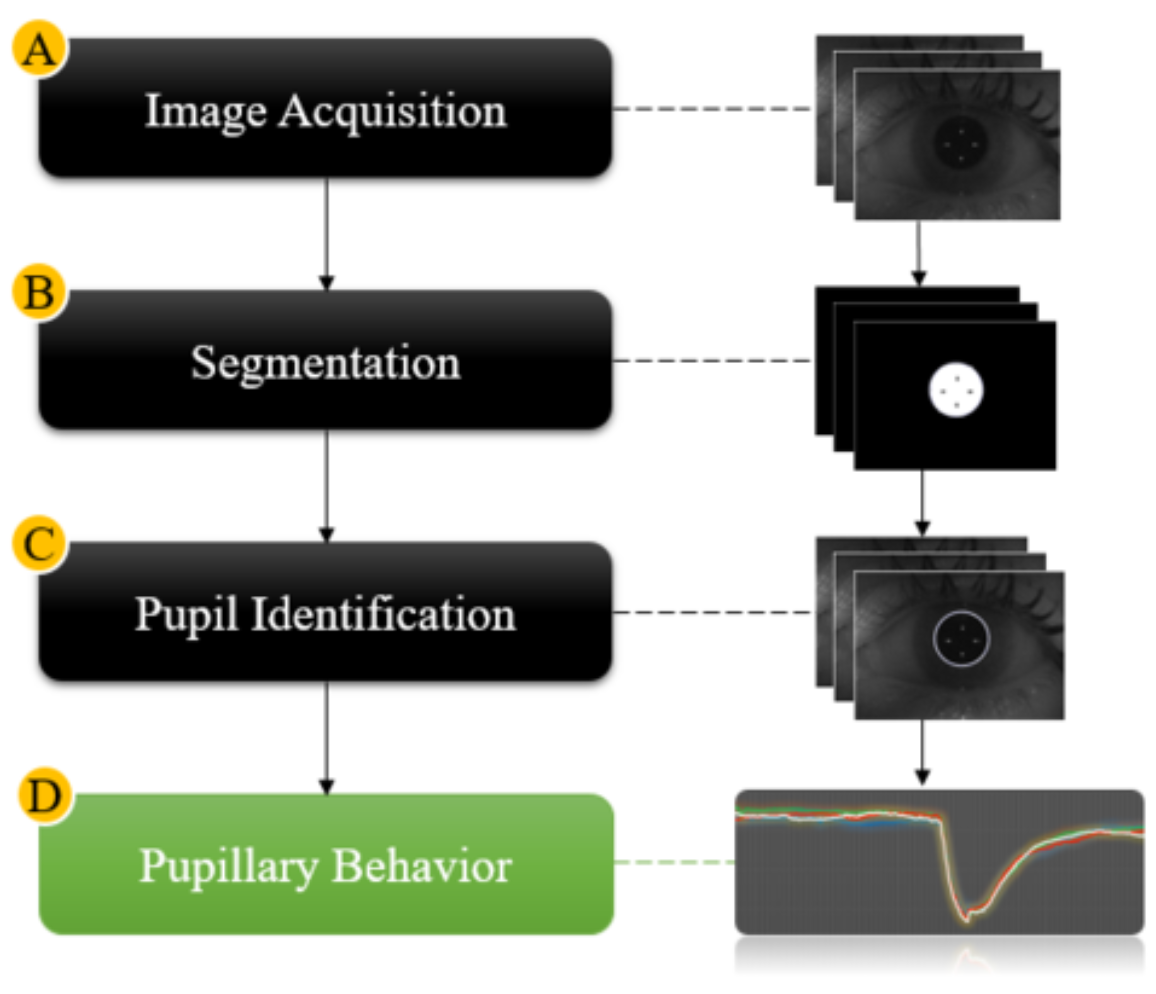
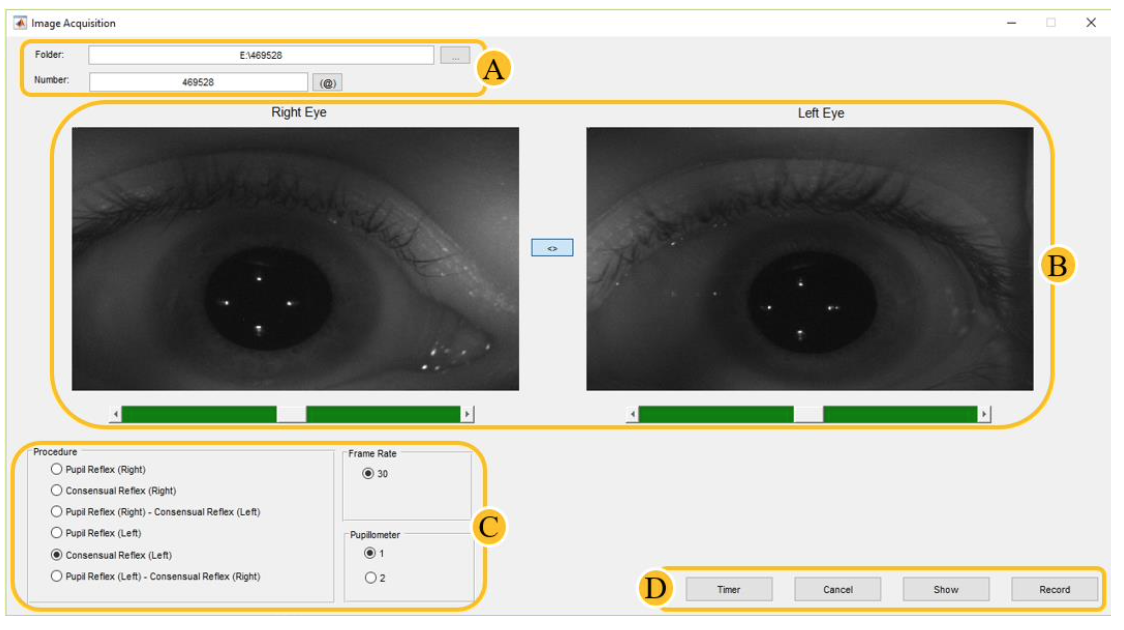
Automated pupillometry is a system used for imaging the pupil that can help diagnose pathologies,
physiological conditions, and cognitive or emotional state.
It also allows to assess interest, effort in decision making, tiredness, fatigue, drug use and autonomic
system functions.
According to research carried out by our group, published in
Jornaul of
Biomedical Informatics
titled
"Pupillary light reflex as a diagnostic aid from computational viewpoint: A systematic literature
review"
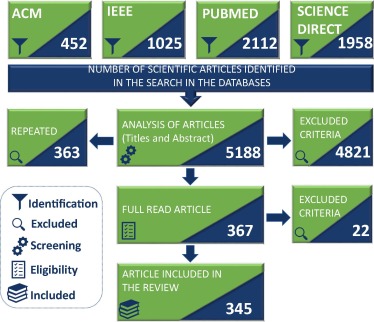
there are approximately 50 different physical conditions or pathologies that have been studied with the aid of
pupillometry.
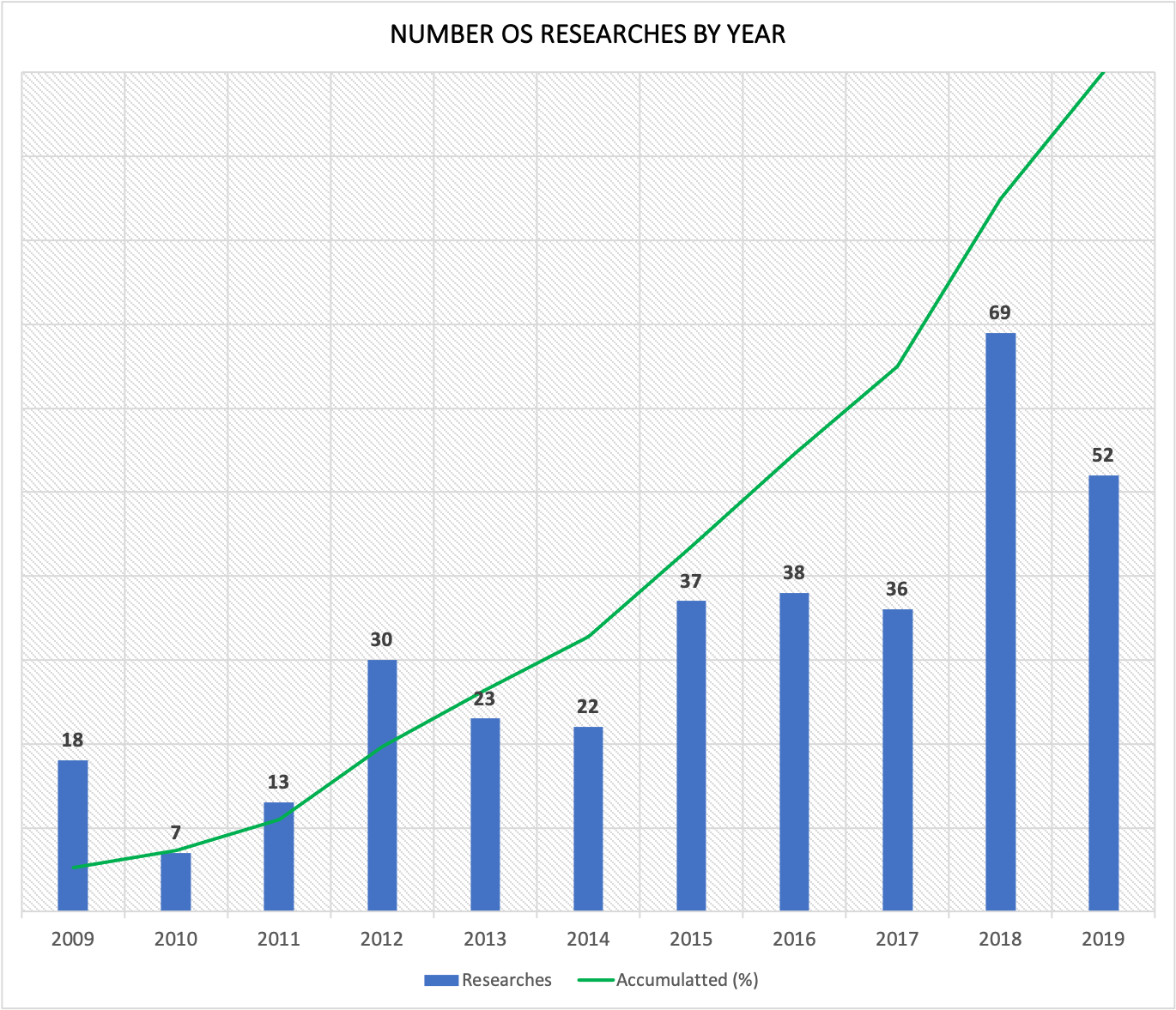
The practicality and assertiveness of pupillometry has aroused the interest of the research community and,
thus, a considerable amount of research has been published in recent years to aid in diagnosis.